Updated on March 15, 2021
Ssh/iddsa debug2: we sent a publickey packet, wait for reply debug1: Server accepts key: pkalg ssh-dss blen 433 debug2: inputuserauthpkok: debug1. Use SSH keys for authentication when you are connecting to your server, or even between your servers. They can greatly simplify and increase the security of your login process. When keys are implemented correctly they provide a secure, fast, and easy way of accessing your cloud server. Find out how to protect your server's sensitive data by learning how SSH keys work, creating an SSH key pair, and creating FTP users in SiteWorx. Dedicated Servers. Built-to-order dedicated infrastructure, customizable for your needs. Cloud Dedicated Servers.
If you spend enough time in an IT environment and with the rise of cloud infrastructure such as AWS, you will likely come across the term SSH keys. If you’ve already come across this IT term, then you might find yourself wondering, what are SSH keys? SSH (Secure Shell) keys are an access credential that is used in the SSH protocol and they are foundational to modern Infrastructure-as-a-Service platforms such as AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure.
Before this post delves into an explanation on what are SSH keys, let’s take a quick look at the SSH protocol.
Try it our way and see for yourself
Ssh Ssh Key
Try JumpCloud's cloud-based directory for user, device and SSO management risk free.
The SSH Protocol
The first version of the SSH protocol was developed in the summer of 1995 by Tatu Ylonen. Tatu was a researcher at the University of Helsinki when a sniffing attack was discovered on the university network. A sniffing attack intercepts and logs the traffic that takes place on a network and can provide attackers with usernames and passwords which can then be used to gain access to critical IT assets. Thousands of credentials were impacted, including those belonging to community partnerships. This sniffing attack motivated Tatu to figure out how to make networks more secure, and this ultimately led to the creation of the SSH protocol (SSH.com).
Today, the SSH protocol is widely used to login remotely from one system into another, and its strong encryption makes it ideal to carry out tasks such as issuing remote commands and remotely managing network infrastructure and other vital system components. This is especially important in the era of cloud infrastructure and remote work. To use the SSH protocol, a couple pieces of software need to be installed. The remote systems need to have a piece of software called an SSH daemon, and the system used to issue commands and manage the remote servers needs to have a piece of software called the SSH client. These pieces of software are necessary to create a proper communication channel using the SSH protocol (DigitalOcean).
Essentially, SSH keys are an authentication method used to gain access to an encrypted connection between systems and then ultimately use that connection to manage the remote system.
What are SSH keys?

SSH keys come in many sizes, but a popular choice is an RSA 2048-bit encryption, which is comparable to a 617 digit long password. On Windows systems, it is possible to generate your own SSH key pair by downloading and using an SSH client like PuTTY. On Mac and Linux systems, it is possible to generate an SSH key pair using a terminal window. Watch the video below to find out how to generate your own RSA key pair on Mac and Linux.
SSH keys always come in pairs, and every pair is made up of a private key and a public key. Who or what possesses these keys determines the type of SSH key pair. If the private key and the public key remain with the user, this set of SSH keys is referred to as user keys. If the private and public keys are on a remote system, then this key pair is referred to as host keys. Another type of SSH key is a session key. When a large amount of data is being transmitted, session keys are used to encrypt this information.
Now let’s take a closer look at how a private key and public key work. To keep things simple, we will focus on how user keys work.
How User Keys Work
In a user key set, the private key remains on the system being used to access the remote system (i.e. the user’s desktop or laptop) and is used to decrypt information that is exchanged in the SSH protocol. Private keys should never be shared with anyone and should be secured on a system – i.e. the system is secured (full disk encryption, MFA), in the user’s possession, and the private key is secured via passphrase.
A public key is used to encrypt information, can be shared, and is used by the user and the remote server. On the server end, the public key is saved in a file that contains a list of authorized public keys. On the user’s side, the public SSH key is stored in an SSH key management software or in a file on their computer.
Using SSH Keys

First Steps
Before you can start using SSH keys, first you need to generate your own SSH key pair on the system you would like to use to access a remote system. This article and the video mentioned above are great resources that can guide you through on how to generate an SSH key pair. Once the key pair is generated, the next step is to put the public SSH key on the remote server. Depending on your setup, this can be done by entering a couple commands in the terminal window, using JumpCloud, or by manually placing the public SSH key on the remote server (DigitalOcean).
Behind the Scenes of SSH Key Authentication
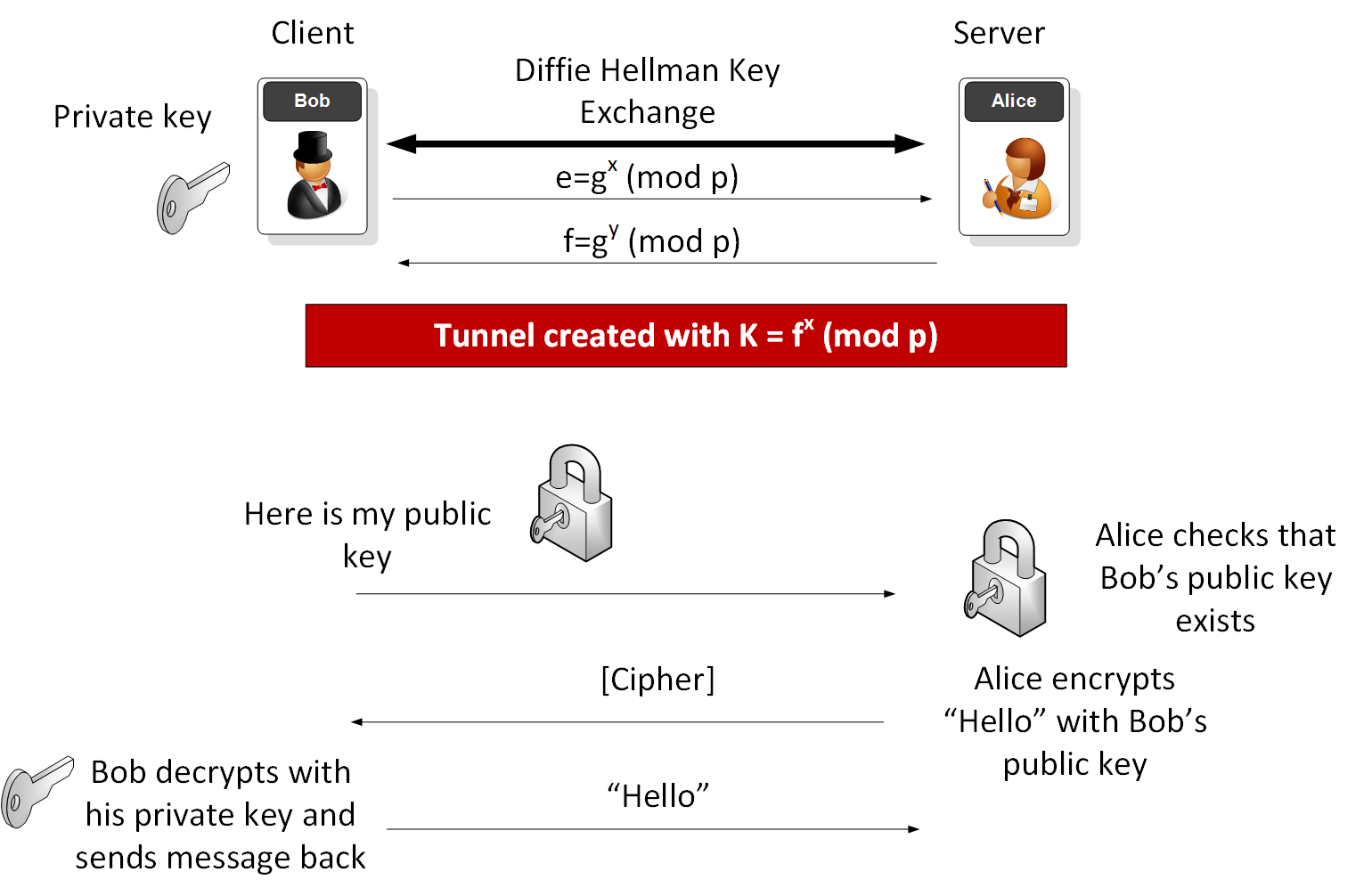
After completing the steps mentioned above, use your terminal to enter in your ssh username and the IP address of the remote system in this format: ssh username@my_ip_address. This will initiate a connection to the remote system using the SSH protocol. The protocol and specified username will then tell the remote server which public key to use to authenticate you. Then the remote server will use that public key to encrypt a random challenge message that is sent back to the client. This challenge message is decrypted using the private key on your system.
Once the message is decrypted, it is combined with a previously arranged session ID and then sent back to the server. Download adobe effects for mac. If the message matches with what the server sent out, the client is authenticated, and you will gain access to the remote server. This process proves to the server that you have the corresponding private key to the public key it has on file.
However, the security that this authentication process provides can be undermined when SSH keys are not properly managed.
Managing SSH Keys
It is imperative that proper SSH key management is in place because they often grant access to mission-critical digital assets. Also, companies tend to have a lot of SSH keys. In fact, Fortune 500 companies will often have several millions of these. Despite the difficulty in trying to manually manage millions of SSH keys, having an SSH key management system in place is continuously overlooked. SSH.com did some digging and discovered a company that had 3 million SSH keys “that granted access to live production servers. Of those, 90% were no longer used. Root access was granted by 10% of the keys ”. An effective SSH key management system in place would have gone a long way in reducing this concerning security risk.
IT has a couple options to gain control over SSH keys in their environment. One of these includes using an SSH key management tool. However this means having to manage one more platforms in addition to managing an SSO provider, a directory service, and maybe a system management solution. A new solution has emerged that is providing IT with a second option: JumpCloud Directory Platform.
Cloud IAM offers SSH Key Management
This cloud-based identity and access management solution provides IT with one central place to manage SSH keys. Furthermore, IT can also centralize user authentication to Mac, Linux, and Windows devices, cloud servers, wired and WiFi networks, web-based and on-prem applications, and virtual and on-prem storage. With one central place to manage a user’s authentication to all of their resources, it becomes a simple matter of a few clicks to deprovision users from all of their resources, including SSH key access to remote systems.
Learn More about SSH Key Management with JumpCloud
You are more than welcome to reach out to us if you would like more information on how the JumpCloud Directory Platform can simplify your SSH key management. If you’re ready to start testing our modern IAM platform, sign up for a free account. You’ll be able to explore all of our features, and your first 10 users and 10 devices are free. We’ll also be happy to help you 24×7 with our premium in-app chat support during the first 10 days.
On Windows, you can create SSH keys in many ways. This document explains how to use two SSH applications, PuTTY and Git Bash.
Joyent recommends RSA keys because the node-manta CLI programs work with RSA keys both locally and with the ssh agent. DSA keys will work only if the private key is on the same system as the CLI, and not password-protected.
PuTTY
PuTTY is an SSH client for Windows. You can use PuTTY to generate SSH keys. PuTTY is a free open-source terminal emulator that functions much like the Terminal application in macOS in a Windows environment. This section shows you how to manually generate and upload an SSH key when working with PuTTY in the Windows environment.
About PuTTY
PuTTY is an SSH client for Windows that you will use to generate your SSH keys. You can download PuTTY from www.chiark.greenend.org.uk.
When you install the PuTTY client, you also install the PuTTYgen utility. PuTTYgen is what you will use to generate your SSH key for a Windows VM.
| This page gives you basic information about using PuTTY and PuTTYgen to log in to your provisioned machine. For more information on PuTTY, see the PuTTY documentation |
|---|
Generating an SSH key
To generate an SSH key with PuTTYgen, follow these steps:
- Open the PuTTYgen program.
- For Type of key to generate, select SSH-2 RSA.
- Click the Generate button.
- Move your mouse in the area below the progress bar. When the progress bar is full, PuTTYgen generates your key pair.
- Type a passphrase in the Key passphrase field. Type the same passphrase in the Confirm passphrase field. You can use a key without a passphrase, but this is not recommended.
- Click the Save private key button to save the private key. You must save the private key. You will need it to connect to your machine.
- Right-click in the text field labeled Public key for pasting into OpenSSH authorized_keys file and choose Select All.
- Right-click again in the same text field and choose Copy.
Importing your SSH key
Now you must import the copied SSH key to the portal.
- After you copy the SSH key to the clipboard, return to your account page.
- Choose to Import Public Key and paste your SSH key into the Public Key field.
- In the Key Name field, provide a name for the key. Note: although providing a key name is optional, it is a best practice for ease of managing multiple SSH keys.
- Add the key. It will now appear in your table of keys under SSH.
PuTTY and OpenSSH use different formats of public SSH keys. If the text you pasted in the SSH Key starts with —— BEGIN SSH2 PUBLIC KEY, it is in the wrong format. Be sure to follow the instructions carefully. Your key should start with ssh-rsa AAAA….
Once you upload your SSH key to the portal, you can connect to your virtual machine from Windows through a PuTTY session.
Git Bash
The Git installation package comes with SSH. Using Git Bash, which is the Git command line tool, you can generate SSH key pairs. Git Bash has an SSH client that enables you to connect to and interact with Triton containers on Windows.
To install Git:
- (Download and initiate the Git installer](https://git-scm.com/download/win).
- When prompted, accept the default components by clicking Next.
- Choose the default text editor. If you have Notepad++ installed, select Notepad++ and click Next.
- Select to Use Git from the Windows Command Prompt and click Next.
- Select to Use OpenSSL library and click Next.
- Select to Checkout Windows-style, commit Unix-style line endings and click Next.
- Select to Use MinTTY (The default terminal of mYSYS2) and click Next.
- Accept the default extra option configuration by clicking Install.
When the installation completes, you may need to restart Windows.
Launching GitBash
To open Git Bash, we recommend launching the application from the Windows command prompt:
- In Windows, press Start+R to launch the Run dialog.
- Type
C:Program FilesGitbinbash.exeand press Enter.
Generating SSH keys
First, create the SSH directory and then generate the SSH key pair.
One assumption is that the Windows profile you are using is set up with administrative privileges. Given this, you will be creating the SSH directory at the root of your profile, for example:
- At the Git Bash command line, change into your root directory and type.
Change into the .ssh directory
C:Usersjoetest.ssh- To create the keys, type:
Ssh Set Key
- When prompted for a password, type apassword to complete the process. When finished, the output looks similar to:
Uploading an SSH key
To upload the public SSH key to your Triton account:
- Open Triton Service portal, select Account to open the Account Summary page.
- From the SSH section, select Import Public Key.
- Enter a Key Name. Although naming a key is optional, labels are a best practice for managing multiple SSH keys.
- Add your public SSH key.
When Triton finishes the adding or uploading process, the public SSH key appears in the list of SSH keys.
Ssh Using Keys
What are my next steps?
Ssh-keygen Ssh-ed25519
- Adding SSH keys to agent.
- Set up the Triton CLI and CloudAPI on Windows.
- Set up the Triton CLI and CloudAPI.
- Create an instance in the Triton Service Portal.
- Set up the
triton-dockercommand line tool. - Visit PuTTYgen to learn more about the PuTTYgen and to seethe complete installation and usage guide.

Comments are closed.