Uranium is used in the nuclear fuel cycle either enriched or depleted in 235 U, hence the annotation 'm'. All uranium isotopes are α-emitters. Isotopes 235 U and 238 U are primordial with the 235 U abundance declining very gradually in geological time because of its faster decay. Uranium is a radionuclide that has an extremely long half-life. Naturally occurring uranium-238 present in the Earth’s crust has a half-life of almost 4.5 billion years. If you take a soil sample anywhere in the world, including your backyard, you will find uranium atoms that date back to when the Earth was formed.
- Uranium Isotopes Percent Abundance
- Uranium Isotopes In Water
- Uranium Isotopes Have Different
- Uranium Isotopes Chart
- Uranium Isotopes Medical
- Natural Uranium Isotope Abundance
- Uranium Isotopes Are Separated By Effusion
The team then extracted the 122-neutron isotope using a magnetic device called a separator. All uranium isotopes undergo α-decay, a process whereby an atom loses two protons and two neutrons. Uranium (U) isotopes (238 U/ 235 U, reported as δ 238 U) in marine carbonates have emerged as an important tool for determining the oxygenation state of ancient oceans. Uranium has sixteen isotopes. All of the isotopes are radioactive. Naturally-occurring uranium contains approximately 99.28305 by weight U-238, 0.7110% U-235, and 0.0054% U-234. The percentage weight of U-235 in natural uranium depends on its source and may vary by as much as 0.1%.
A radioactive and strategic element
The uranium atom is the heaviest atom present in the natural environment. Its radioactivity is very low. Its very long life of several billion years has allowed uranium to be still present. It is a rare chemical element found in the Earth's crust with an average of 3 grams per tonne.
The uranium image has suffered from its association with the first atomic bombs. Its reputation as a malevolent radioisotope, however, is undeserved: in fact, the decay rate of uranium is among the slowest known to man. H safari for mac. The activity of a sample of uranium could be compared to the water flow escaping from a pond through a pinprick.
Martin Heinrich Klaproth (1743-1817) was a German chemist best known for his discovery of a variety of chemical elements, including the 1789 discovery of uranium, zirconium and chromium. He is sometime credited as being the ‘father of analytical chemistry’.
DR
These reassuring features not prevent this unfortunate element to be regularly presented by TV channels as a dangerous radioactive substance ? Or is our complacence born of ignorance? Contrary to the widespread fears, uranium presents low risks owing to its very low radioactivity. Its radioactive toxicity, according to experts from the CEA, is a hundred times weaker than its chemical toxicity, which itself is no different from the chemical danger posed by common heavy elements such as lead.
Uranium Isotopes Percent Abundance
Athabasca plateau in Saskatchewan province, Canada. Western Canada is particularly rich in uranium, with anywhere between 28 to 210 kilograms of uranium per tonne as opposed to the usual 3 grams per tonne found elsewhere. This high abundance, taken in conjunction with the difficult geological conditions and the harsh climate have made the extraction process an almost entirely automated one.
HARRY GRUYAERT /MAGNUM /AREVA
 Though both isotopes were at the time of Earth formation equally abundant, natural uranium today consists today of 99.3% uranium 238 and only 0.70% uranium 235. The nuclei of uranium 235 and 238 are, along with those of thorium 232, the heaviest present in nature. They were all formed billions of years ago by the explosion of heavy stars (supernovae).
Though both isotopes were at the time of Earth formation equally abundant, natural uranium today consists today of 99.3% uranium 238 and only 0.70% uranium 235. The nuclei of uranium 235 and 238 are, along with those of thorium 232, the heaviest present in nature. They were all formed billions of years ago by the explosion of heavy stars (supernovae).The radioactivity of uranium is low, and so no particularly high standards of radioprotection are needed: as can be seen with the above workmen. The concentrated uranium they are handling, also known as ‘Yellow Cake’, takes the form of a bright yellow powder containing about 750kg of uranium per tonne. This high concentration makes it much easier to transport the uranium from the mine to the factory. The photograph above shows the ‘yellow cake’ on a filter at a treatment plant in Jouac (Haute-Vienne) at Limousin, France.
PHILIPPE LESAGE/COGEMA
As a particularly heavy element, uranium isotopes are primarily alpha emitters, though these radiations are sometimes accompanied by gamma rays.
Uranium Isotopes In Water
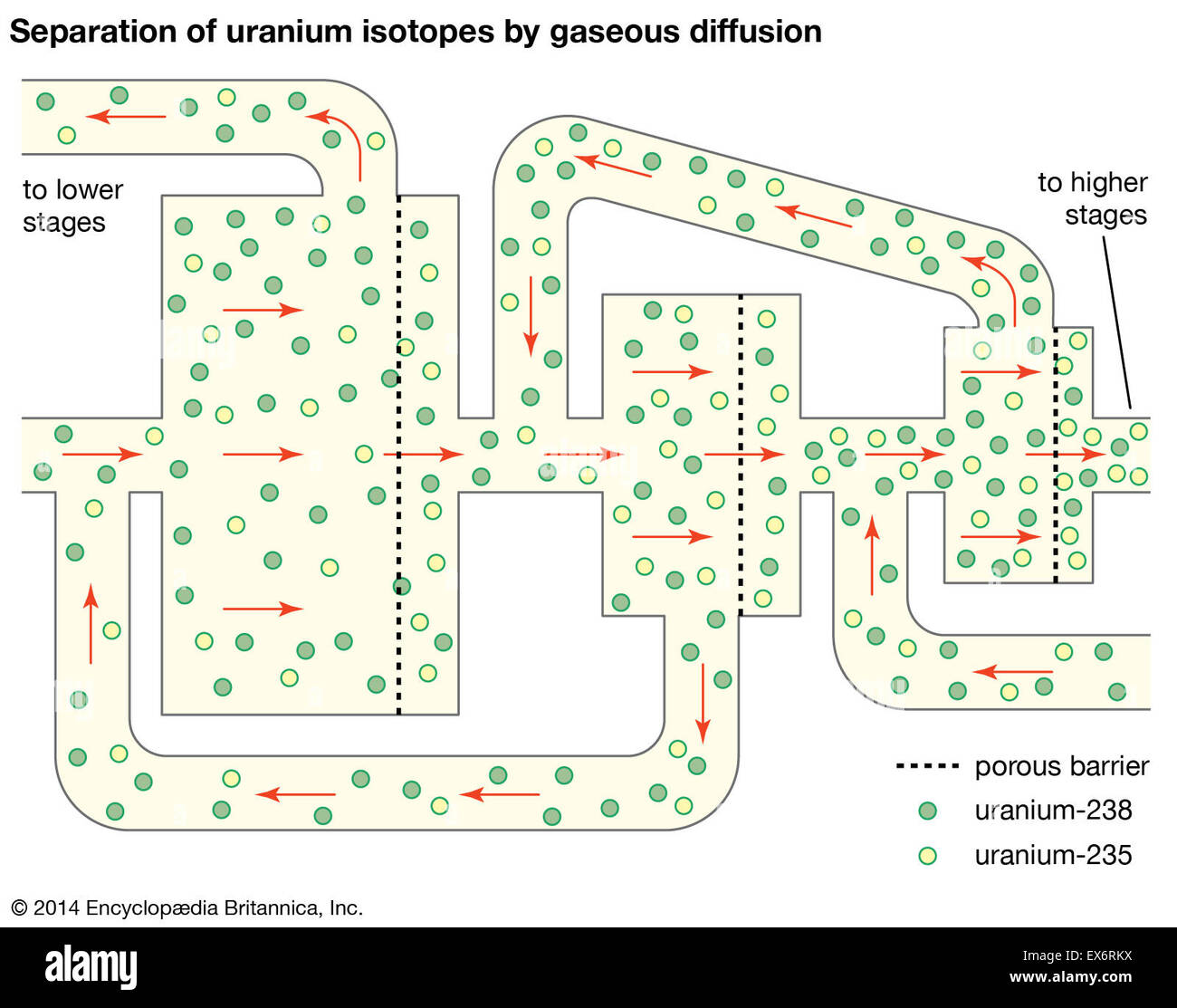
Natural uranium is poor in the fissile isotope, containing as it does only 0.70% of uranium 235. It must be enriched before it can be used as a fuel in any commercial reactor. These reactors are powered by uranium which is enriched to have anywhere between 3 and 4% of uranium 235. In order to have an atomic bomb, the uranium has to be enriched to above 90%. The boundary between the uranium meant for civilian uses (LEU or low-enriched uranium) and that uranium meant for military use (HEU or highly-enriched uranium) is generally fixed at 20%.
IN2P3
 Uranium 235 is the only natural nucleus that can easily undergo fission. Highly sought-after, it can be used as a fuel in nuclear reactors and as an explosive in atomic bombs.
Uranium 235 is the only natural nucleus that can easily undergo fission. Highly sought-after, it can be used as a fuel in nuclear reactors and as an explosive in atomic bombs.The more abundant uranium 238 is sometimes called fertile. Fission occurs comparatively rarely, and even under bombardment with energetic neutrons the probability of fission remains very low. What happens more frequently is that a neutron capture causes the nucleus to become unstable. After a few days, uranium 239 has transformed into plutonium 239, a radioisotope with a half-life of 24,000 years. Plutonium 239 is highly fissile and can also be used as a nuclear fuel or an atomic explosive.
Uranium reserves which exist under the oceans are about a thousand times more abundant than the reserves found in high quality minerals on land. Underwater uranium, however, would be extremely costly to exploit.
TO KNOW MORE ABOUT URANIUM AND ITS USES :
- 1) :
Uranium Isotopes Have Different
Isotopes de l'uranium- 2) :
 Uranium fuels
Uranium fuels- 3) : Propriétés de l'uranium
Uranium Isotopes Chart
Uranium Isotopes Medical
Access to page in frenchNatural Uranium Isotope Abundance
Uranium Isotopes Are Separated By Effusion
Nuclear Fission
Fissile nuclei
Isotopic Separation

Comments are closed.